The Importance of Reading and Understanding Statistics Correctly – Case of Foreign Direct Investments

photo credit: Corporate Finance Institute
Foreign Direct Investments are one of the most important factors for a country’s economic development. Therefore, investment statistics have always been a matter of discussion both in political and academic circles. Given the significance of the issue, statistics are often reported manipulatively from different media sources which can happen deliberately, be influenced by populism or precipitated by the lack of competence. Therefore, it is vital to broaden academic discussion and offer more clear explanations to the people how the investment statistics should be read.
On 10 March 2023, the National Statistics Office of Georgia published a preliminary report of foreign direct investments in Georgia for 2022. According to the statistics, USD 2 billion investments were made to Georgia in 2022 which at the first glance is a record-high figure. However, other variables should definitely be taken into account in order to draw conclusions and have correct assessment of foreign direct investment indicator.
What is Foreign Direct Investments (FDI), what benefits does it bring and how should we read the statistics?
Foreign Direct Investments are long-term capital investments in securities, real estate and production, made by non-resident physical or legal persons. FDI consists of three major components:
- Stock Capital or Charter Capital
- Reinvestment
- Debt obligations
These three components, in turn, consist of: (1) founding a new company, (2), acquisition or selling share in operational company, (3) acquisition or selling real estate, (4) profit and loss incurred as a result of entrepreneurial activity (5) issuing dividend (6) borrowing, lending or paying debt and (7) supplying goods and services.
Foreign Direct Investments bring multiple benefits, including job creation. Any new investment means putting additional resources into a country whereas resource requires management, processing, inventory or use of other type of human input. Therefore, more investment means more employment. Another important positive factor are foreign currency inflows. More foreign currency on the one hand positively affects balance of payments and on the other hand it means more income and stronger national currency. Any new investment promotes and increases competition. This is reflected in lower prices, higher quality of goods and services, technological progress and sectoral improvements. All these positive effects are aggregated into an economic growth – the most important criteria for a country.
Speaking of Foreign Direct Investments, it is necessary to underline those factors which positively or/and negatively affect attracting the FDI. These factors can be divided into two main categories:
- How property and property rights are protected in a country;
- How big is a legislative interference in the process of disposing private property.
No country, irrespective of its form of governance, will be able to attract investments if property rights are not protected. Protection of property rights, however, are directly linked with such factors as follows:
- Geopolitical situation – country’s political and economic situation is a single most important factor for investments. The higher the chances of force-majeure (such as war, coup d’état, conflict areas, etc.), the less incentivized is an investor to start business in such country.
- Independence and efficiency of the judiciary – court disputes, be it property-related or between the private sector representatives and the government, often take place in every country and society. An investor would pick a country where the court will make fair ruling and his/her property will not be unjustly expropriated or damaged. In addition, the court should effectively deal with disputes and the so-called court overload issue should also be taken into account. Since time is money, the more a dispute is protracted, the costlier it is for both sides.
- Crime rates – under market economy, to make sure that business produces wealth, fair rules should unavoidably be in place that would protect property and activity of all business from racketeering, robbing, stealing, illegal financial schemes and other types of criminal activities.
- Corruption level – investor will make a decision based on cost-benefit analysis of him/her investing in a country and starting business there. The higher corruption level a country has, the costlier it is for an investor.
Protection of property is the most important factor to attract investments, but a country’s legislative framework also needs to be reckoned with. It is possible that a country has a rule of law, but still remains less attractive for the investments. Such factors are as follows:
- Tax burden – higher taxes means less incentives for an investor to make investments. Number of taxes, as well as tax rates are both important. For instance, there are six types of taxes in Georgia whereas tax burden is nearly 25%, meaning the government disposes every GEL 25 from each GEL 100 generated in the country. The less tax burden, the higher is the incentive for international and local business to invest.
- Government effectiveness and transparency – together with number and size of taxes, it is key that the government can effectively collect them, tax authorities work in a transparent manner and process is as much automatized as possible. More barriers mean bigger expenses for an investor.
- Financial sustainability – apart from current situation in the country, each investor carefully analyzes past and potential of a country, since most of investment projects are designed for long-term prospects. The less budget deficit and government debt as well as the better macroeconomic indicators are, the higher is a fiscal health which sends a positive signal to any investor.
- Regulatory framework – any government regulation is associated with a specific expense which business needs to incur. The higher economic regulations are in the country, the costlier it is for a potential investor to start business and production. Each regulation requires regulatory analysis to take into consideration additional costs calculated in GEL (or/and in other currencies) for the investors.
A country which will meet as many criteria from the abovementioned list as possible will successfully attract more investments.
Chart 1: Foreign Direct Investments in 1996-2022 (USD Million)
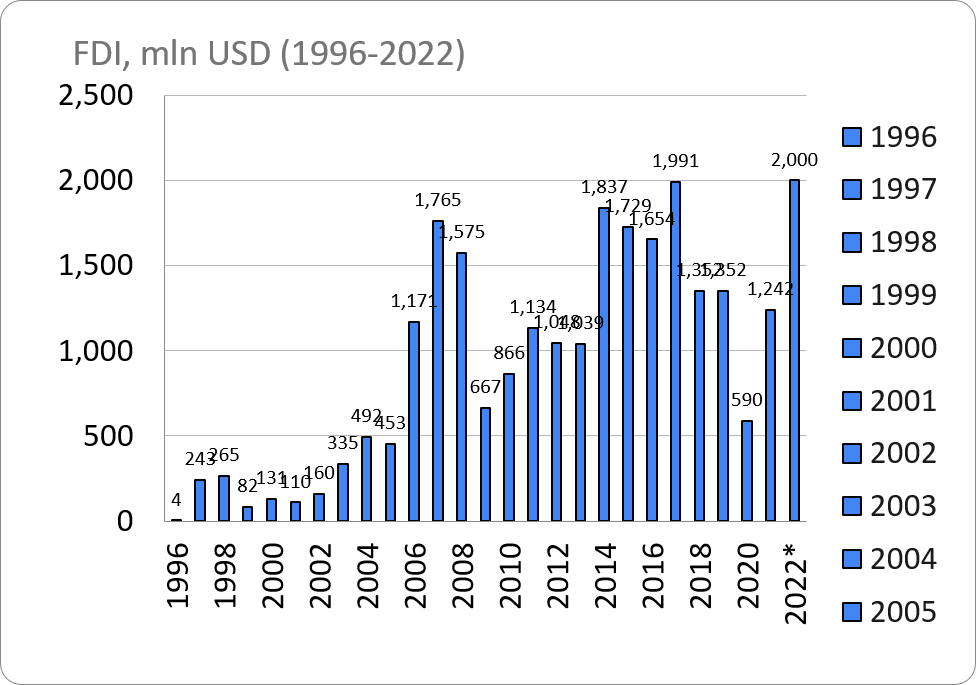
Source: National Statistics Office of Georgia
Chart 1 clearly shows that FDI inflows to Georgia are not markedly stable. The highest nominal volumes of investments were registered in 2007, 2017 and 2022 whereas the lowest FDI figures were registered in 1999-2022. A country’s economy grows over the years and in order to maintain economic growth, bigger economy needs bigger investments. As a result, comparison of nominal investment figures from different years is hardly justified. We can see a better picture when annual FDI growth rates are compared to each other which is shown at Chart 2.
Chart 2: Foreign Direct Investments Growth Rate (1998-2022)
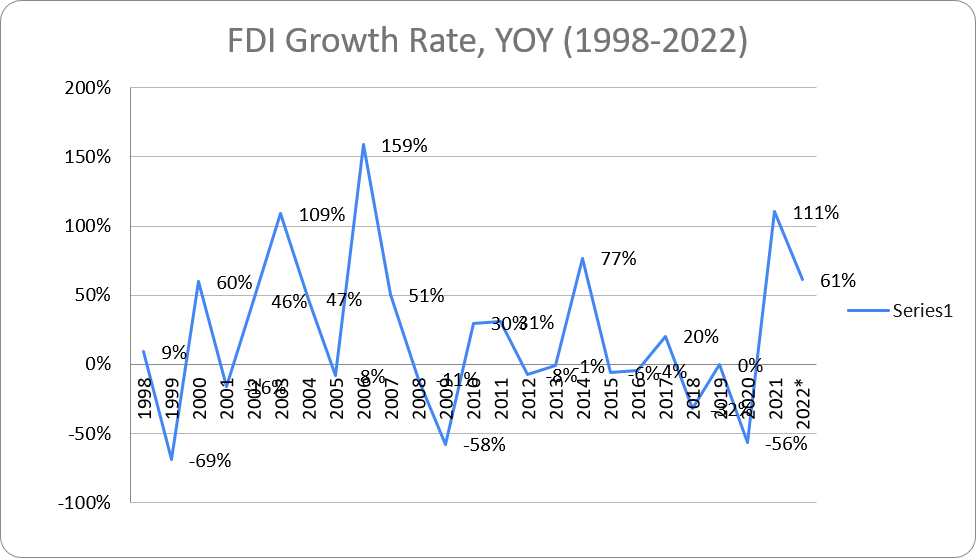
Source: National Statistics Office of Georgia
Apart from comparison of FDI growth rates over the years, the most economically sound approach vis-à-vis analysis of statistics is measuring Foreign Direct Investments to GDP ratio. As a country’s economy grows it requires more investment every next year. For instance, we can have a look at two countries – USA and Georgia. Georgia’s economy in 2022 is nearly USD 24.7 billion whereas US economy is 950 times bigger and amounts to USD 23.3 trillion. Hypothetically, USD 25 billion investment would nearly double Georgia’s economy whereas for the US it would be merely 0.08% of its economy, ushering a deep economic crisis there. Therefore, investments to GDP ratio is the most important element when analyzing investments.
Chart 3: Foreign Direct Investments and FDI to GDP Ratio (1997-2022)
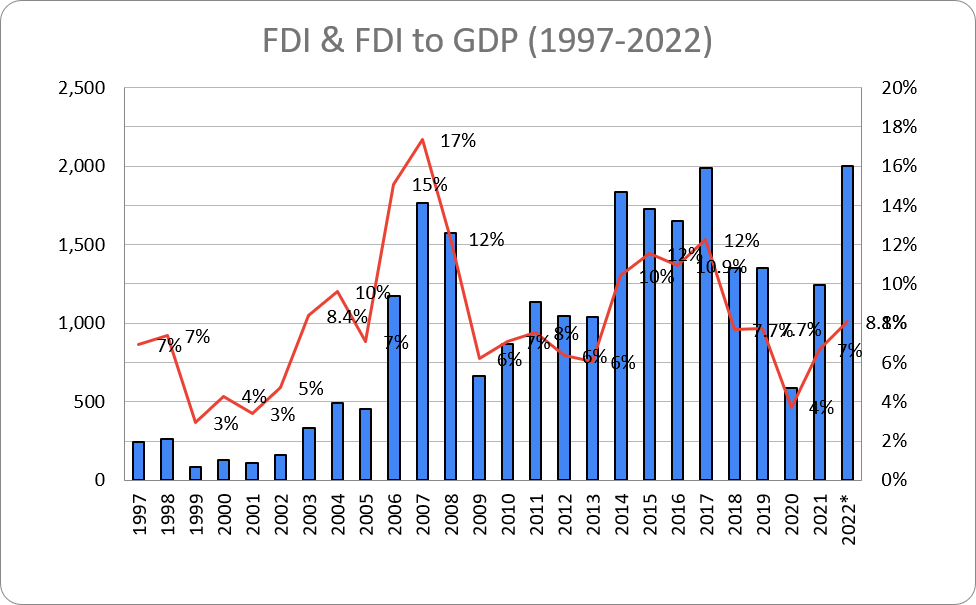
Source: National Statistics Office of Georgia, author’s calculations
Chart 3 clearly illustrates that nominal figure of Foreign Direct Investments can be high or even record-high in a specific year, but the picture can be completely opposite when it comes of FDI to GDP ratio. For instance, record-high USD 2 billion in 2022 is 8.1% of total economy and in 2003, nominal investments were USD 335 million, although FDI to GDP ratio stood at 8.4%. Of note is that 2006 and 2007 were most successful years when FDI to GDP ratios were 15% and 17%, respectively.
***
In conclusion, it is possible to say that Foreign Direct Investments play a key role in a country’s economic development. They are a factor behind employment and average wage growth rate, price level, technological progress and myriad other positive elements which directly influence quality of life. In turn, attracting investments is related to a number of important components, such as property rights, independent and efficient judiciary, corruption level, crime, number of taxes and regulations, inflation rate, etc. Therefore, it is very often that instead of subject-matter discussions on why investments are scarce, FDI figures are subjected to manipulation and economically unfavorable situation may be portrayed as a success. To avoid this, it is important to read statistics correctly which is equally needed for civil sector and media as well as for any individual who takes interest in economic themes. Oftentimes, nominal figures do not say anything. It is necessary to have year-over-year comparison and analysis in line with a country’s development indicators. To this aim, the most telling criterion would be Foreign Direct Investments to gross domestic product ratio.
See the attached file for the entire document with relevant sources, links and explanations.


